Getting Started (Java)
This tutorial explains all the steps needed to get started developing applications that interact with Content Server using the CWS API with Java and Eclipse.
Outline
- Create a New Project
- Create CWS Client Proxies
- Using the Services
- Run the Program
- Source Code
- References
Create a New Project
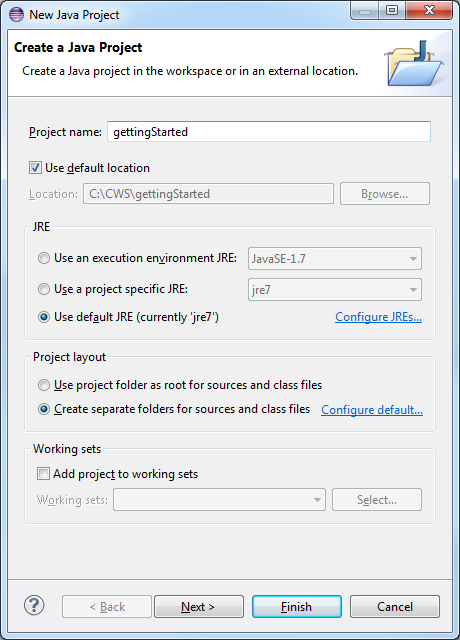
The first thing we need is a new project in Eclipse to work with.
-
Open Eclipse.
-
Open the File menu and select New → Java Project.
-
Enter a name for the project and then select Finish.
Create CWS Client Proxies
Next, we need create the client proxies for each CWS service we want to use.
-
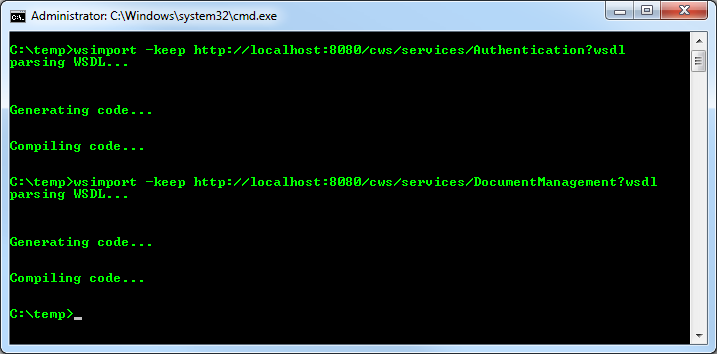
Open a new command prompt.
-
Use the wsimport command to generate the client proxies for each service. Enter the following commands:
wsimport -keep http://localhost:8080/cws/services/Authentication?wsdlwsimport -keep http://localhost:8080/cws/services/DocumentManagement?wsdl -
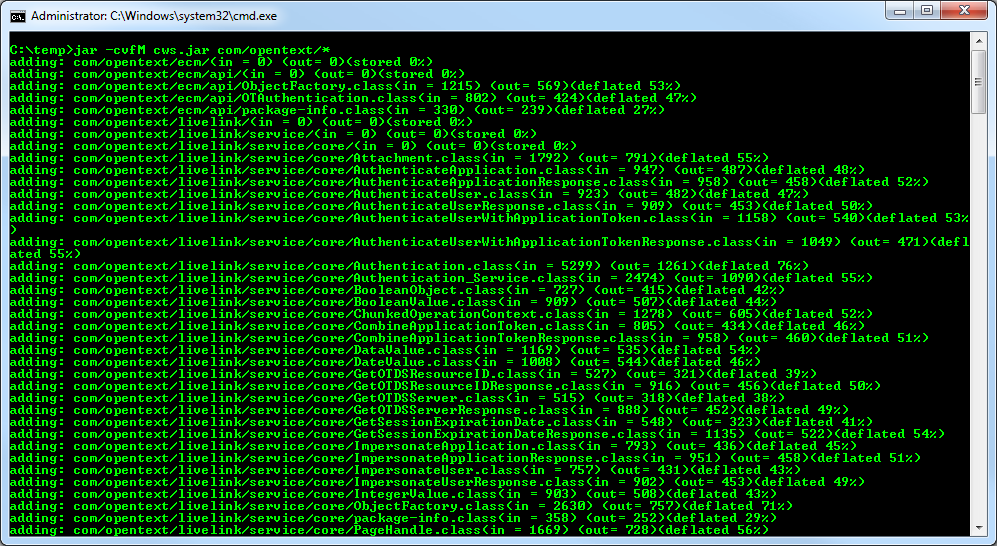
Use the jar command to bundle the generated class files into a .jar file. Enter the following command:
jar cvfM cws.jar com/opentext* -
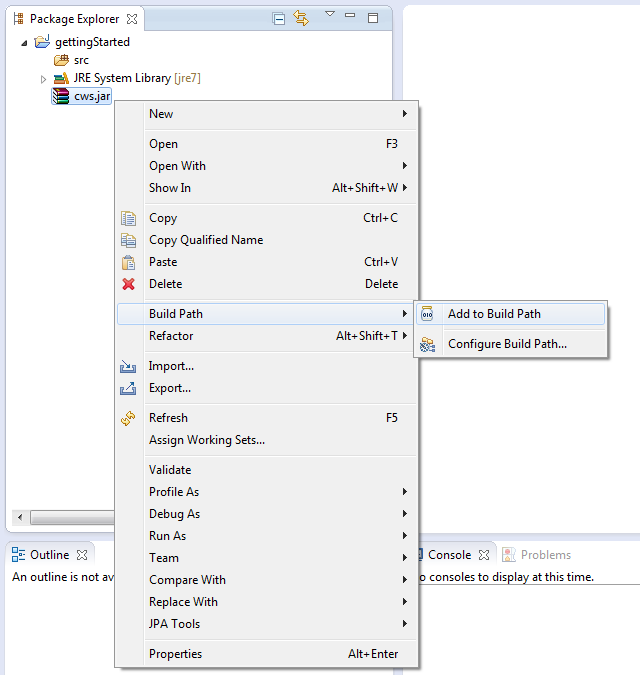
Copy the cws.jar file into your eclipse project and add it to your build path by right clicking the cws.jar file in the Package Explorer and select Build Path → Add to Build Path.
Using the Services
Now that the CWS services are ready to use we can go ahead and start writing some code. The first thing to do is to authenticate a user. To get started here we will use basic Content Server authentication using the CWS Authentication service. You will need to change the USERNAME and PASSWORD to use valid credentials of a user on your system.
// The user's credentials String USERNAME = "username"; String PASSWORD = "password"; // Create the Authentication service client Authentication_Service authService = new Authentication_Service(); Authentication authClient = authService.getBasicHttpBindingAuthentication(); // Store the authentication token String authToken = null; // Call the AuthenticateUser() method to get an authentication token try { System.out.print("Authenticating User..."); authToken = authClient.authenticateUser(USERNAME, PASSWORD); System.out.println("SUCCESS!\n"); } catch (SOAPFaultException e) { System.out.println("FAILED!\n"); System.out.println(e.getFault().getFaultCode() + " : " + e.getMessage()); return; }
The other CWS services are all similar in the way they are used.
- Create a service client.
- Create an OTAuthentication object to pass along the authentication token with each request. To do this we need to manually set the SOAP headers on the service client.
- Use the service client to call operations on the service.
Here is an example using the DocumentManagement service to get a user's favorites:
// Create the DocumentManagement service client DocumentManagement_Service docManService = new DocumentManagement_Service(); DocumentManagement docManClient = docManService.getBasicHttpBindingDocumentManagement(); // Create the OTAuthentication object and set the authentication token OTAuthentication otAuth = new OTAuthentication(); otAuth.setAuthenticationToken(authToken); // We need to manually set the SOAP header to include the authentication token try { // The namespace of the OTAuthentication object final String ECM_API_NAMESPACE = "urn:api.ecm.opentext.com"; // Create a SOAP header SOAPHeader header = MessageFactory.newInstance().createMessage().getSOAPPart().getEnvelope().getHeader(); // Add the OTAuthentication SOAP header element SOAPHeaderElement otAuthElement = header.addHeaderElement(new QName(ECM_API_NAMESPACE, "OTAuthentication")); // Add the AuthenticationToken SOAP element SOAPElement authTokenElement = otAuthElement.addChildElement(new QName(ECM_API_NAMESPACE, "AuthenticationToken")); authTokenElement.addTextNode(otAuth.getAuthenticationToken()); // Set the SOAP header on the docManClient ((WSBindingProvider) docManClient).setOutboundHeaders(Headers.create(otAuthElement)); } catch (SOAPException e) { System.out.println("Failed to set authentication SOAP header!\n"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.out.println(e.getStackTrace()); return; } // Store the favorites List<Node> favorites = null; // Call the getAllFavorites() method to get the user's favorites try { System.out.print("Getting the user's favorites..."); favorites = docManClient.getAllFavorites(); System.out.println("SUCCESS!\n"); } catch (SOAPFaultException e) { System.out.println("FAILED!\n"); System.out.println(e.getFault().getFaultCode() + " : " + e.getMessage()); return; } // Output the user's favorites System.out.println("User's Favorites:\n"); if (favorites.size() > 0) { for (Node node : favorites) { System.out.println(node.getName()); } } else { System.out.println("No Favorites."); } System.out.println();
Run the Program
If everything is setup correctly you should be able to successfully run the program.